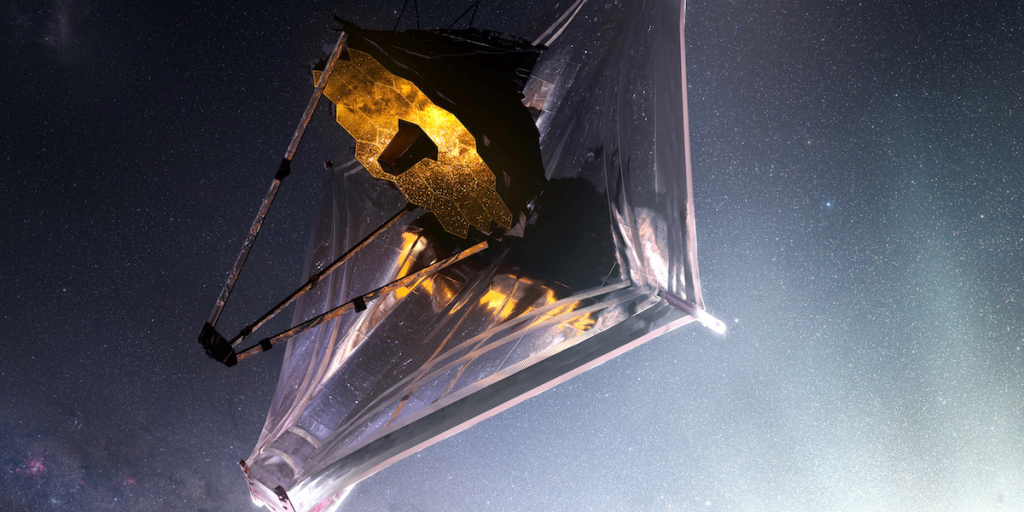
Mission
“ Through the Looking GLASS: A James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Exploration of Galaxy Formation and Evolution from Cosmic Dawn to Present Day
Grism Lens-Amplified Survey from Space (GLASS) is one of JWST Director’s Discretionary Early Release Science Programs, and will be focused on two main science areas: (1) understanding the reionization of the universe less than 1 billion years after the Big Bang: (2) understanding how gas and heavy elements are distributed (chemical abundance) within and around galaxies over time.
Focus Area
(1) Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. In the fields of Big Bang theory and cosmology, reionization is the process that caused matter in the universe to reionize after the lapse of the “dark ages” which began around 370,000 years after the Big Bang. During the Dark Ages, the temperature of the universe cooled from some 4,000 (K)elvin to about 60 K (3,727 °C to about −213 °C) and though the universe was transparent it was dark, as only two sources of photons (visible light) existed: (a) the photons released during recombination or decoupling (as neutral hydrogen atoms formed), which we can still detect today as the cosmic microwave background (CMB); (b) photons occasionally released by neutral hydrogen atoms.
While the majority of baryonic matter in the universe is in the form of hydrogen and helium, reionization usually refers strictly to the reionization of hydrogen. Baryonic matter is a type of composite subatomic particle which contains an odd number of valence quarks (at least 3) and belong to the hadron family of particles which includes protons and the neutrons.
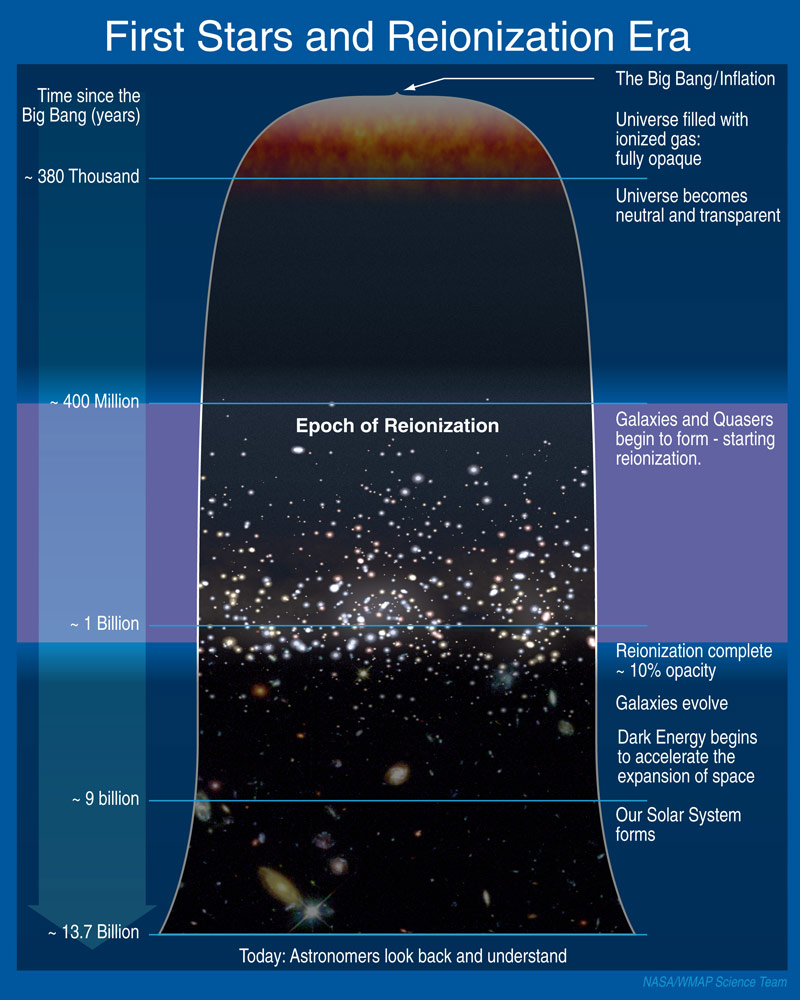
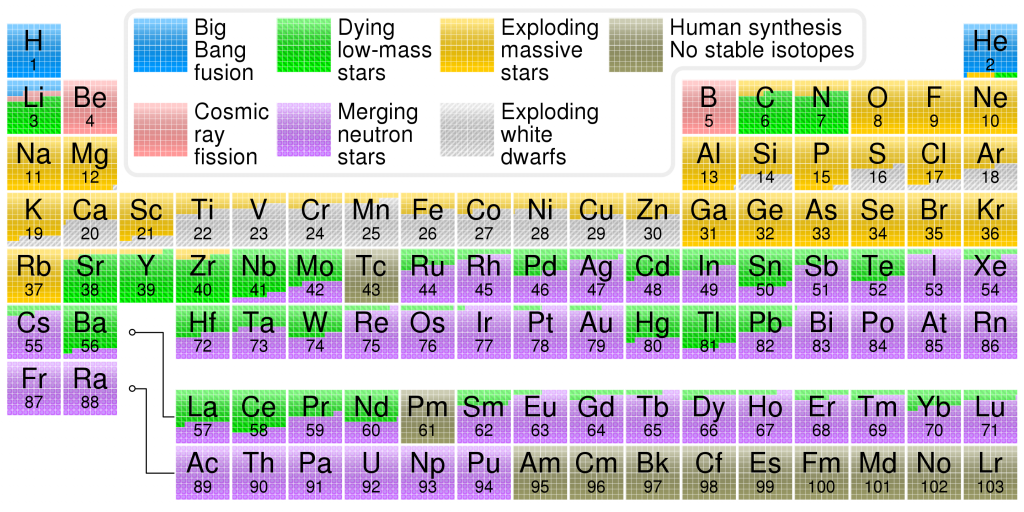
(2) The abundance of the chemical elements is a measure of the occurrence of the chemical elements relative to all other elements in a given environment. The abundance of chemical elements in the universe is dominated by the large amounts of hydrogen and helium which were produced in the Big Bang. Remaining elements, making up only about 2% of the universe, were largely produced by supernovae and red giant stars.
Method
GLASS will combine the natural magnifying power of gravitational lensing, caused by the massive galaxy cluster Abell 2744 (one of the Frontier Fields), with JWST’s incredible sensitivity to measure detailed properties of distant galaxies in the early universe.
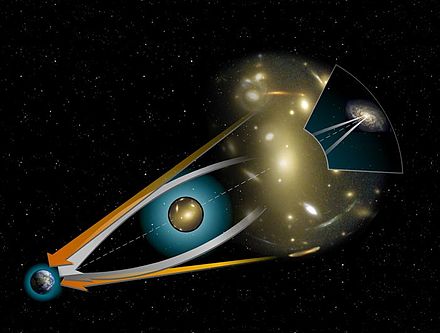
Abell 2744, nicknamed Pandora’s Cluster, is a giant galaxy cluster resulting from the simultaneous pile-up of at least four separate, smaller galaxy clusters that took place over a span of 350 million years. It is located approximately 4 billion light years from Earth. The galaxies in the cluster make up less than five percent of its mass. The cluster’s gas (accounting for around 20 percent of the cluster’s mass) is so hot that it shines only in X-rays. And dark matter makes up the remaining 75 percent of the cluster’s mass.
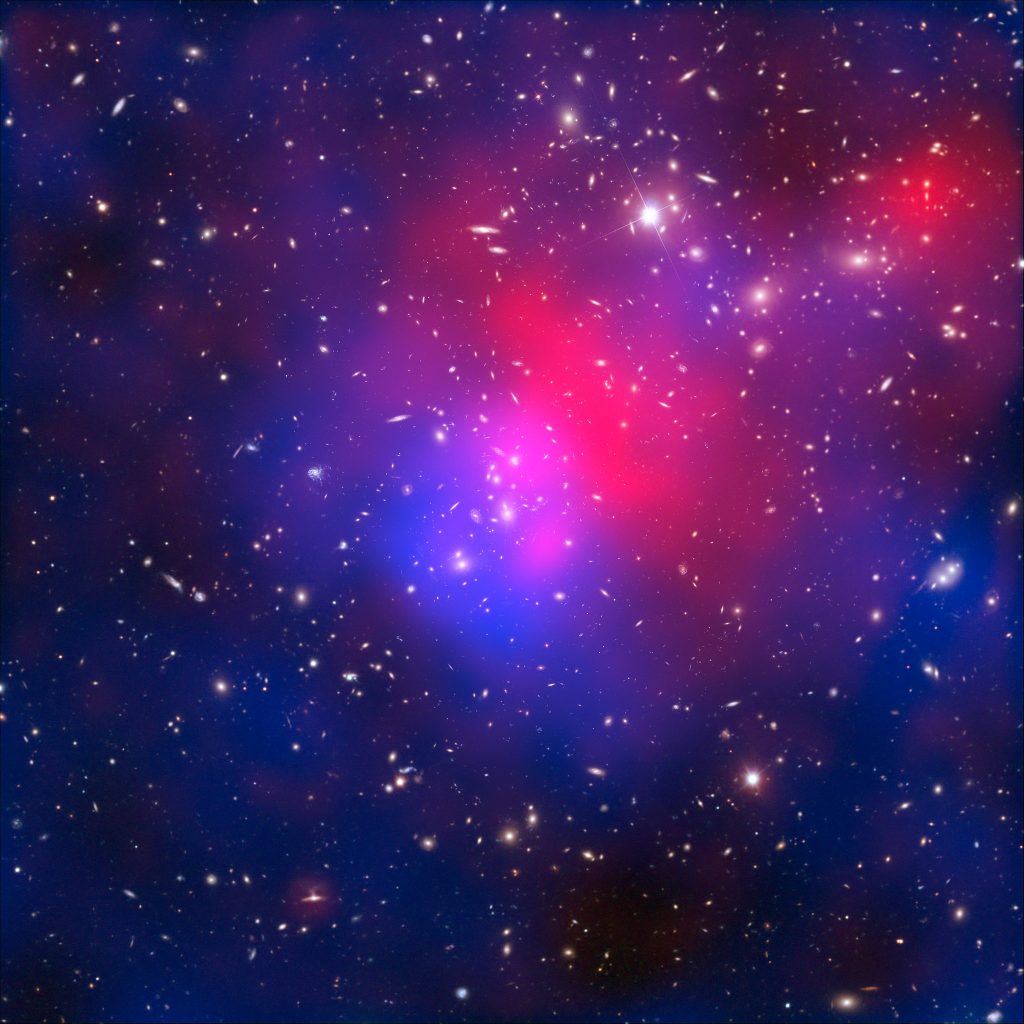

Dark matter does not emit, absorb, or reflect light, but it makes itself apparent through its gravitational attraction. To pinpoint the location of this elusive substance gravitational lensing is exploited. A gravitational lens is a distribution of matter (such as a cluster of galaxies) between a distant light source and an observer, that is capable of bending the light from the source as the light travels toward the observer. This bending of light rays from distant galaxies as they pass through the gravitational field created by the cluster forms a series of telltale distortions in the images of galaxies observed in the background of observations from the Hubble and Very Large Telescope (VLT). The mass of Abel 2744 will act as a sort of massive but distant focal lense.
Key Science Drivers
(1) To shed light upon the role of galaxies in reionizing the universe, the topology of high redshift intergalactic/interstellar medium and on Lyman alpha escape fraction. A redshift is an increase in the wavelength, and corresponding decrease in the frequency and photon energy, of electromagnetic radiation (such as light). The opposite change, a decrease in wavelength and simultaneous increase in frequency and energy, is known as a negative redshift, or blueshift. The value of a redshift is often denoted by the letter z, corresponding to the fractional change in wavelength (positive for redshifts, negative for blueshifts), and by the wavelength ratio 1 + z (which is >1 for redshifts, <1 for blueshifts). It is commonly believed that galaxies at z ≳ 5 are the dominant sources for cosmic reionization. The escape fraction of Lyman-continuum (LyC), or hydrogen ionizing photons from these galaxies is hence an important question for understanding the reionization process.
(2) To study: (a) gas accretion, the accumulation of particles into a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter); (b) star formation and outflows by mapping spatially resolved star formation, where spatial resolution is a measure of the smallest object that can be resolved by the sensor; (c) metallicity, the abundance of elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium) gradients in galaxies at z = 1.3 – 2.3.
(3) To study the environmental dependence of galaxy evolution.
References: Space Telescope Science Institute glass.astro.ucla.edu NASA Wikipedia: Reionization; Abel 2744; Chemical Abundance; Gravitational lens
